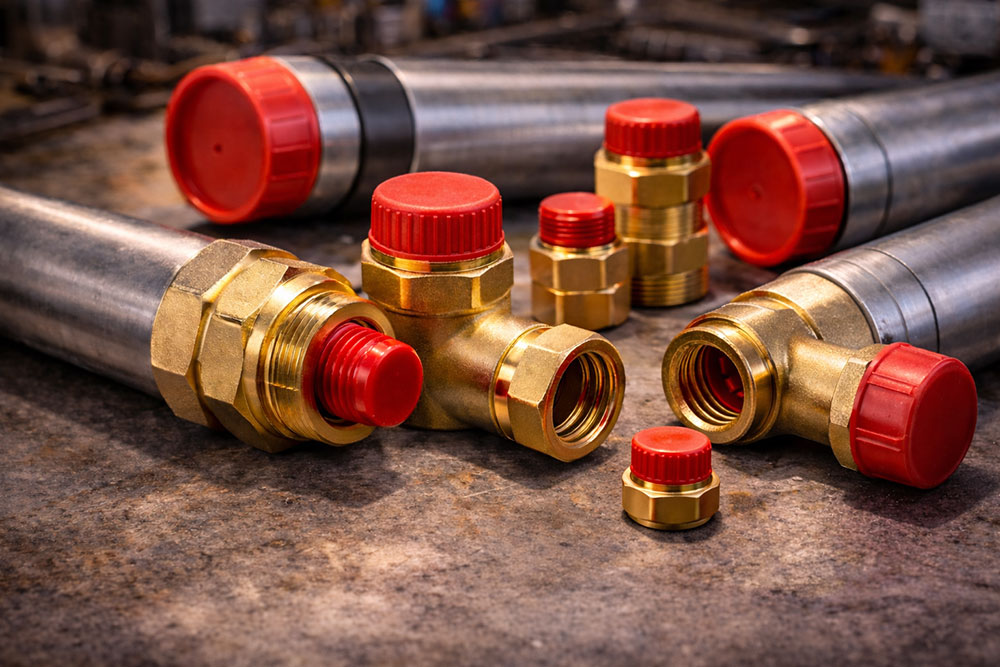
What Are Cap Plugs?
Cap plugs (sometimes called plastic caps or protective plugs) are simple components with a big job: they cover open ends of pipes, tubing, and threaded fittings to prevent damage, contamination, or leaks.
Choosing the wrong cap or plug can lead to costly repairs, unexpected downtime, or safety hazards. That’s why proper selection is critical for maintenance and engineering professionals.
These components are used across maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO), in manufacturing, and during storage or shipping. A well-chosen cap plug keeps equipment clean, safe, and ready for immediate use.
Common Materials
Cap plugs come in a range of materials, each suited for different applications:
- Vinyl: Lightweight and flexible. Ideal for temporary protection.
- Rubber: Offers impact resistance and a tighter seal when needed.
- Polypropylene / Plastic: Chemical- and moisture-resistant. Perfect for general protection.
- Silicone (High-Temp): Handles heat, powder-coating, and painting processes without degrading.
Why Cap Plugs Are Critical
Even a single uncapped pipe end can cause debris to accumulate, fluid leaks to form, or metal surfaces to corrode.
Cap plugs maintain clean lines during downtime and protect threaded fittings from damage. They also reduce the risk of injury from sharp edges and keep contamination out during storage or transport.
From the Ram Products Experts
“One low-cost plug can stop a chain reaction of problems. During hydraulic or motor repairs, capping open ports keeps debris out but also prevents unexpected high-pressure discharge if the system is powered prematurely. Plus, it cuts down on fluid leaks from disconnected hoses to protect the equipment and workspace.”
![[H3]-melting-cap](https://ramproducts.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/H3-melting-cap.jpg)
The Most Common Misconceptions
Cap plugs are simple, but they can be used incorrectly.
Technicians frequently pick the wrong size or thread type, which can cause poor protection or fit. Some choose materials that can’t handle heat, chemicals, or other harsh conditions. Understanding the differences is key to keeping equipment safe.
From the Ram Products Experts
“Brass caps and plugs use pipe thread, not USS bolt threads, which throws people off. Steel caps and plugs follow a different sizing system entirely, measured in 1/16-inch increments. For example:
- A #4 steel plug equals ¼ inch (four 1/16ths)
- A ½-inch plug is a #8 (eight 1/16ths)
Understanding those two systems eliminates most of the sizing confusion we see.”
For a full range of plastic caps and plugs, shop Cap Plugs at Ram Products.
Common Uses in MRO (and Missed Opportunities)
Cap plugs aren’t just small accessories; they solve real problems in MRO. Properly applied, they keep equipment running smoothly, protect components during downtime, and prevent costly mistakes.
At the same time, failing to use them in the right places creates missed opportunities for preventing damage, contamination, or safety issues.
“One place I consistently see cap plugs overlooked is during motor rebuilds. Technicians will leave open cavities uncapped, and that’s a perfect opportunity for dirt or debris to get inside. Using plugs during rebuilds is critical for protecting internal components and preventing avoidable damage.”
Product Expert, Ram Products
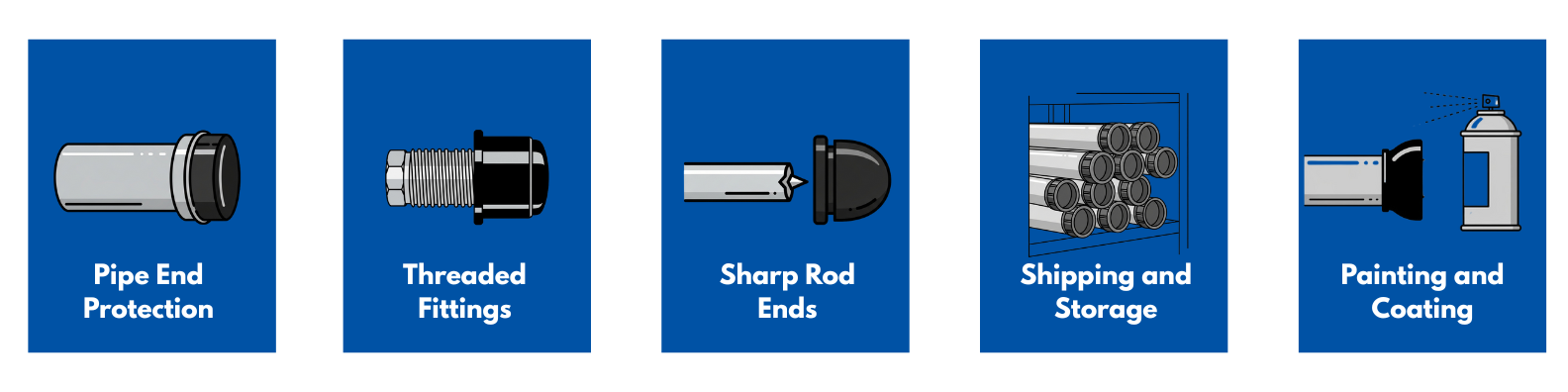
Typical Applications
- Pipe End Protection: Cap plugs keep debris, dirt, and moisture out of pipelines during construction, maintenance, or storage.
- Threaded Fittings: Plugs protect threads on bolts, hydraulic lines, or other fittings when equipment is disassembled.
- Sharp Rod Ends: Vinyl or rubber caps cover exposed rods or tubing, reducing the risk of injury and damage.
- Shipping and Storage: Plastic caps prevent contamination and scratches during transport or while equipment sits in storage.
- Painting and Coating: High-temp silicone plugs can be used to mask openings during powder-coating or painting processes.
How Cap Plugs Save Your Assets (and Prevent Big Problems)
Even a single uncapped pipe or fitting can let in debris, cause leaks, or damage expensive components.
Installing cap plugs correctly prevents larger, costlier issues down the line. They’re fast to install, often reusable, and are a highly cost-effective way to protect your equipment.
Types of Cap Plugs
Cap plugs come in a variety of designs, each suited for specific applications. Understanding the differences helps maintenance and engineering professionals choose the right protection for their pipes, tubes, and fittings.
Push-On Caps (and Push-In Caps)
Push-on caps are simple, flexible, and easy to install. They fit snugly over the outside diameter of a pipe or tube. Push-in caps are installed internally. Both are ideal for temporary or light-duty protection from dirt, moisture, and minor damage during storage or transit.
Quick Takeaways:
- Quick to install and remove
- Flexible materials allow slight variations in diameter
- Best for short-term protection or applications without high pressure
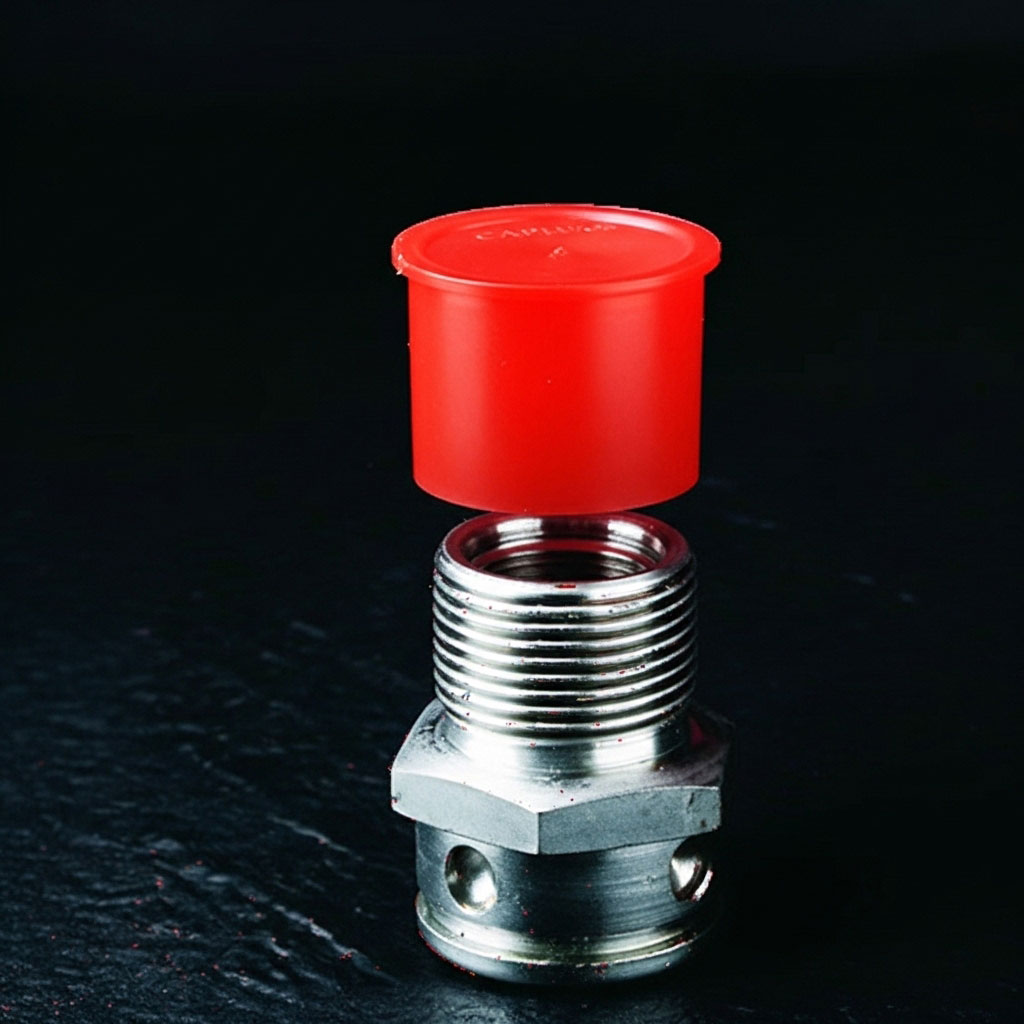
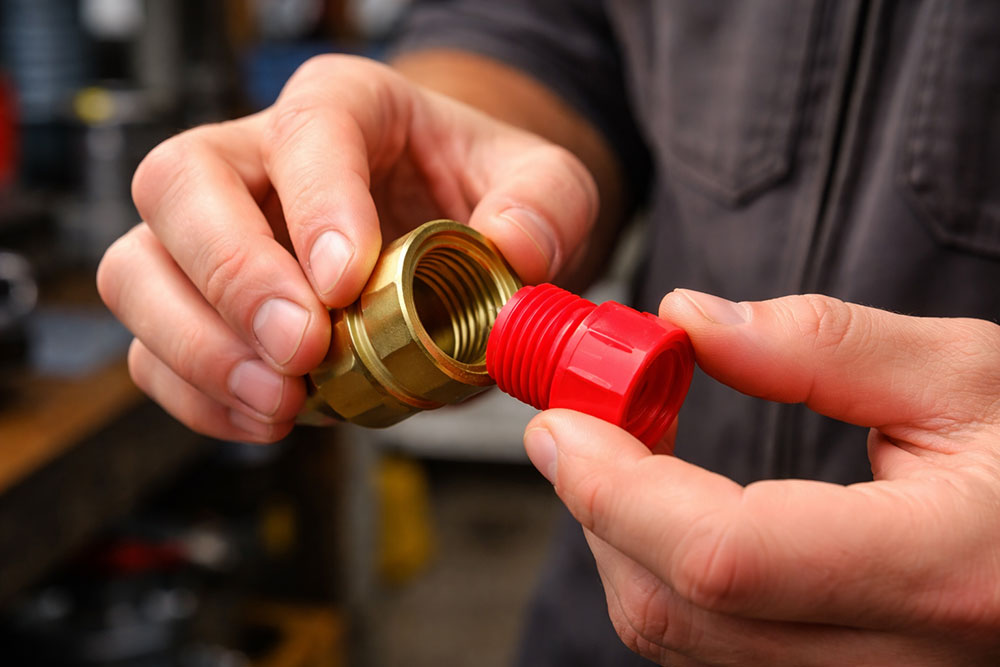


Threaded Plugs
Threaded plugs insert into the end of a pipe or fitting for a secure seal. They are ideal for protecting threads on bolts, hydraulic lines, or piping systems that may experience pressure or movement.
Quick Takeaways:
- Provide a tighter seal than push-on caps
- Available in multiple thread types (NPT, BSPT, etc.)
- Durable for repeated use and harsh conditions
Flange Covers
Flange covers are used to protect flanged pipe ends during transport, storage, or maintenance. They prevent debris from entering the piping system and safeguard the flange faces from scratches or damage.
Quick Takeaways:
- Often made from heavy-duty plastic or rubber
- Useful in industrial or construction applications
- Can be temporary or semi-permanent depending on the material


High-Temp Silicone Caps
High-temp silicone caps are designed for environments with heat or chemical exposure. They are frequently used during powder-coating, painting, or baking processes to mask openings and prevent contamination.
Quick Takeaways:
- Resist high temperatures without deforming
- Chemically resistant and flexible
- Ideal for masking openings or for temporary sealing in manufacturing
The Expert’s Guide to Cap Plug Sizing
Choosing the right size is one of the most critical steps in ensuring cap plugs work effectively. A plug that’s too loose can fall off, letting debris in or causing leaks. One that’s too tight may be difficult to install or remove. It could also damage the pipe or fitting.
Getting the fit right isn’t just about measuring diameter. Thread type, wall thickness, and the shape of the opening all affect performance. Accurate sizing ensures the cap or plug protects your equipment and performs reliably over time.
Fit and Material Considerations
Different materials expand or contract with temperature changes. So, even if measurements are correct, the actual fit can vary depending on material flexibility and environmental conditions.
Vinyl caps stretch slightly for a snug fit, while rigid polypropylene plugs require precise sizing. Testing a sample before large-scale use helps ensure everything works as expected.
“Brass is used on brass fittings. Steel is used on hydraulic systems. Plastic is primarily used on engines.”
Product Expert, Ram Products
For a full range of sizes and protective solutions, explore Cap Plugs at Ram Products.
Buying Tips and Best Practices for the Pros
Selecting the right cap plugs is only half the battle. How you store, handle, and install them can make a big difference in performance and longevity.
Technicians should treat cap plugs as essential components (rather than afterthoughts) to prevent avoidable damage and downtime.
Care About Quality
Durable materials and proper construction are vital. Vinyl, rubber, polypropylene, and high-temp silicone each serve different purposes depending on the application.
Low-cost or flimsy plugs may seem like a budget option but often fail under stress, leading to damaged pipes, fittings, or threads. Investing in high-quality cap plugs upfront saves time, money, and frustration in the field.
Pro Tips:
- Choose plugs made from materials that suit your temperature, chemical, and mechanical requirements.
- High-quality options usually offer consistent sizing and easier installation.
- Inspect new plugs for defects before use.


Versatility & Coverage
Think ahead about the range of applications you need to cover. Some cap plugs are more versatile than others, making them a better investment for multiple tasks.
Professionals often find that buying a versatile plug reduces the number of different sizes and types needed on-site.
Pro Tips:
- Select a plug type that can handle multiple applications without compromising performance.
- Keep an assortment of sizes and materials to meet varying needs.
- Consider color-coding or labeling to simplify identification during maintenance.
Tried-and-True Installation Tips
Proper installation ensures cap plugs do their job and last longer. Even the best plug can fail if installed incorrectly. Small steps during handling, storage, and installation go a long way in preventing problems.
Pro Tips:
- Test-fit a sample plug before bulk use.
- Maintain a ready assortment of sizes for quick access.
- Label or color-code plugs to avoid mix-ups during busy operations.
- Factor in environmental conditions (e.g., heat or chemical exposure), which can affect material performance.
Cap Plug Summary & Practical Takeaways
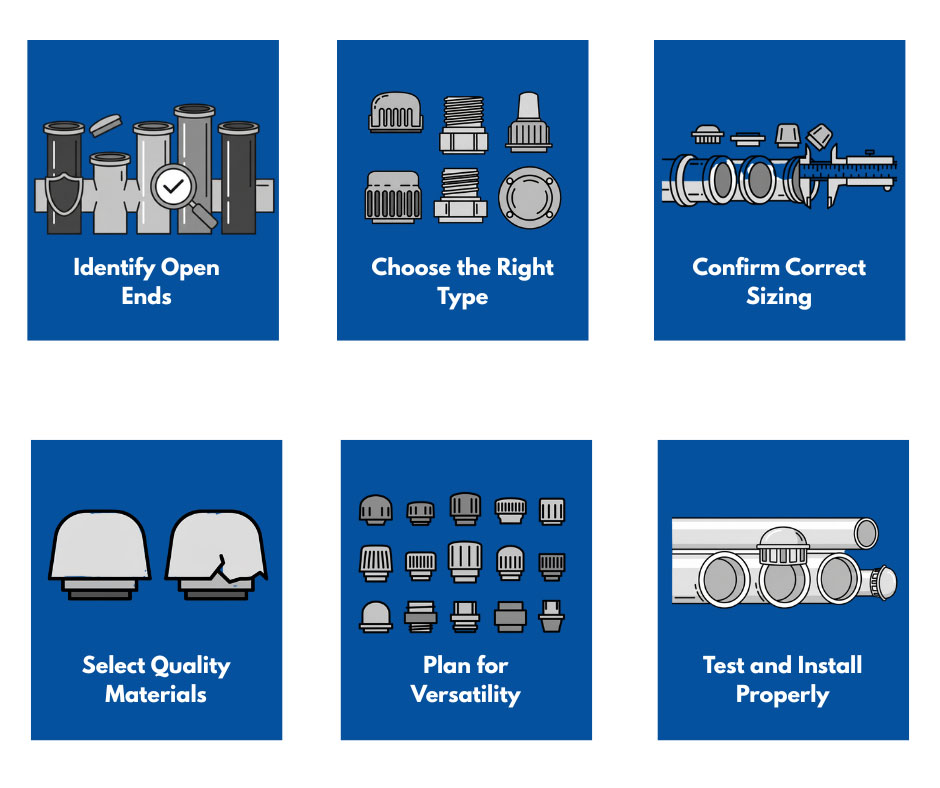
Cap plugs may be small, but their impact is enormous. Use this checklist as a final reference to make sure your pipes, tubes, and fittings are fully protected.
Final Checks Before You Install or Stock Cap Plugs
Identify Open Ends: Inspect all pipes, tubes, rods, and fittings in storage, transit, or operation. Mark or note locations where caps or plugs are missing.
Choose the Right Type: Push-on caps are for temporary, light-duty protection. Threaded plugs are for secure sealing of threads and fittings. Flange covers are for industrial or construction applications. High-temp silicone caps are for masking during painting, coating, or heat exposure.
Confirm Correct Sizing: Measure outside diameter (OD) for caps and inside diameter (ID) for plugs. Check thread type and pitch for threaded plugs. Account for material expansion/contraction in extreme temperatures.
Select Quality Materials: Durable vinyl, rubber, polypropylene, or silicone based on application needs. Avoid cheap or flimsy options that may tear, warp, or fail.
Plan for Versatility: Keep a mix of sizes and materials for multiple applications. Consider universal plugs if stocking one type for multiple tasks.
Test and Install Properly: Test-fit samples before bulk use. Label or color-code plugs to prevent mix-ups. Ensure environmental conditions (heat, chemicals) won’t compromise the material.
Train Your Team: Make sure technicians understand sizing, material selection, and installation best practices. Review common misconceptions to prevent errors on the job.
Stay stocked and ready with our full selection of Cap Plugs from Ram Products.